cmos, analog , design-15
Transcript of cmos, analog , design-15
-
8/10/2019 cmos, analog , design-15
1/362 2005 IEEE International Solid-State Circuits Conference 0-7803-8904-2/05/$20.00 2005 IEEE.
ISSCC 2005 / SESSION 3 / BACKPLANE TRANSCEIVERS / 3.2
3.2 A 6.4Gb/s CMOS SerDes Core withFeedforward and Decision-FeedbackEqualization
M. Sorna1, T. Beukema2, K. Selander1, S. Zier1, B. Ji1, P. Murfet3,J. Mason3, W. Rhee2, H. Ainspan2, B. Parker2
1IBM, East Fishkill, NY2IBM, Yorktown Heights, NY3IBM, Hursley, United Kingdom
Increasing clock rates of processing cores with continuing advances in silicon technology drives the need to push inter-chipI/O to ever higher data rates. As industry-standard data ratespass 3Gb/s and approach the 6+Gb/s to 11+Gb/s [1] realm, degra-dations from channel effects such as bandwidth loss, reflections,and crosstalk can distort the signal to such an extent that reliabledata recovery requires equalizer-based I/O core designs [2]. Inthis paper, the architecture and design of key components of aCMOS 4.9 to 6.4Gb/s 2-level SerDes I/O core which employs a 4-tap feed-forward equalizer (FFE) in the transmit section and a 5-tap decision-feedback equalizer (DFE) in the receive section, isdescribed. A single PLL macro drives up to 4 TX/RX pairs and
generates the reference 4.9 to 6.4GHz clock for the system. Thedesign is realized in 0.13 m CMOS technology using Cu/Al inter-connects.
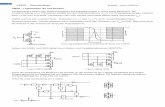
A diagram of the transmitter is shown in Fig. 3.2.1. To minimizediffusion capacitance load at the driver output, the FFE tapweights are sized to maximum weights of 0.25, 1.0, 0.5, and 0.25for the pre-cursor through final tap settings. If a desired FFEsetting cannot be contained within the fixed tap weight range,the main cursor tap can be backed off from full-scale to accom-modate the FFE setting. The tap weights can be either pro-grammed to fixed values or optionally adapted on power-up using an up-channel link protocol. An automatic level control algorithmscales the transmit drive level so the peak-to-peak output voltagemaintains a fixed programmed setting as tap values change. Thedriver swings up to 1200mV ppd into a 100 differential load. A typical 6.4Gb/s transmission demonstrates a total jitter (TJ) of 34ps pp for BER
-
8/10/2019 cmos, analog , design-15
2/3
-
8/10/2019 cmos, analog , design-15
3/3585 2005 IEEE International Solid-State Circuits Conference 0-7803-8904-2/05/$20.00 2005 IEEE.
ISSCC 2005 PAPER CONTINUATIONS
Figure 3.2.7: Die micrograph of 4-port TX/RX core.