Wissenschaftliche Basis des SRA – Analyseverfahrens
Transcript of Wissenschaftliche Basis des SRA – Analyseverfahrens

Stroke-Risik-Analysis - SRAclinic® Version 03 20.11.2017 – All previous version are no longer valid Seite 1
SRAclinic®
Report
Identification from patients with atrial fibrillation or an increased risk for paroxysmal atrial fibrillation
apoplex medical technologies GmbH Delaware Ave. 1-3 66953 Pirmasens Tel. 06331 - 6989980 Fax. 06331 - 69899819 www.apoplexmedical.com [email protected]

Stroke-Risik-Analysis - SRAclinic® Version 03 20.11.2017 – All previous version are no longer valid Seite 2
Contents
General information about SRAclinic®
The SRAclinic® Report
Results of SRAclinic®
Interpretation of Results
Management of SRAclinic® (web platform)
Appendix
SRAclinic® for the detection of AF after a stroke
The Lorenz Plot
Notes on Signal Quality

Stroke-Risik-Analysis - SRAclinic® Version 03 20.11.2017 – All previous version are no longer valid Seite 3
General information about SRAclinic®
In the clinical routine, it is important to obtain clearly arranged and understandable
information for the often difficult creation of the risk profile of a patient to be able to set the
best possible individual treatment concept as quickly as possible.
Especially in patients after a cryptogenic stroke, it is particularly important to initiate effective
therapy to detect potential paroxysmal atrial fibrillation (AF).
Our goal with SRAclinic® is to enable fully automated risk analysis in the simplest and most
reliable way with very little work (especially compared to manual long-term ECG analysis)
over a long period of time.
In the study Rizos et al. in Stroke1, it could be shown that this objective has been achieved
with impressive results. Thanks to automated ECG monitoring during the stay of the patients
in the stroke unit, approx. 40% more patients with paroxysmal AF were detected than in the
previous routine with 24 hours long-term ECG and checking patient monitors. In comparison
to the 24 hour long-term ECG evaluation, an increase of 170% could even be achieved.
On one hand, the success of SRAclinic® is based on the fact that the maximum available
recording time of patient ECGs is used and on the other hand because the underlying
algorithm automatically detects patients with existing fibrillation episodes with a similar
quality as if a cardiologist were to analyze all of these ECGs. This results in a very high
detection rate of patients with manifestation of fibrillation episodes with very little work. In
addition, the algorithm examines the ECG for possible deviations in the sinus rhythm, which
indicate fibrillation episodes that occurred in the past (PLOS One Study2) and is noted as a
risk for paroxysmal atrial fibrillation in the report.
SRAclinic® is a web-based system required for analyzing a two channel, digital long-term
ECG. This is sent to the central SRAclinic® server via the Internet, evaluated completely
automatically, and the result of this risk analysis is documented in a report as PDF.
Afterwards, it is the sender as an attachment via email.
Because SRAclinic® is used primarily in an environment of clinical intensive care medicine,
the use of the ECG data from the patient monitoring system is an obvious option. At present,
there are interfaces for connecting the SRAclinic® application to systems of the
manufacturers Dräger, Philips and Nihon Kohden. For users who do not have one of these
systems in use, the ECG recordings can be made with conventional long-term ECG
recorders.
1 Timolaos Rizos, Janina Güntner, Ekkehart Jenetzky, Lars Marquardt, Christine Reichardt, Rüdiger Becker, Roland Reinhardt, Thomas Hepp,
Paulus Kirchhof, Elena Aleynichenko, Peter Ringleb, Werner Hacke and Roland Veltkamp; Continuous Stroke Unit Electrocardiographic
Monitoring Versus 24-Hour Holter Electrocardiography for Detection of Paroxysmal Atrial Fibrillation After Stroke. 2 Schaefer JR, Leussler D, Rosin L, Pittrow D, Hepp T (2014) Improved Detection of Paroxysmal Atrial Fibrillation Utilizing a Software-Assisted
Electrocardiogram Approach. PLoS ONE 9(2): e89328. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0089328

Stroke-Risik-Analysis - SRAclinic® Version 03 20.11.2017 – All previous version are no longer valid Seite 4
The SRAclinic® Report in connection with:
Dräger and Nihon Kohden patient monitoring systems
In connection with the patient monitoring systems from Dräger and Nihon Kohden, the
SRAclinic® Reports are transmitted completely automatically once per day. In this case, you
receive the complete analysis of the previous day for all patients, for whom an identification
number has been entered on the monitoring system.
Philips patient monitoring system
In connection with a Philips patient monitoring system, the ECG data of the selected patient
are transmitted once every day. The time of the data transmission can be freely selected, but
it has been shown in practice that a transmission in the morning makes sense. You receive
SRAclinic® of the selected patient up to the previous 24 hours.
Long-term ECG recorder
SRAclinic® analyzes up to a maximum of 72 hours of ECG recordings in the case of the use
of long-term ECG recorders. After submission of the ECG, a SRAclinic® for the recorded
period is created and then transmitted immediately.

Stroke-Risik-Analysis - SRAclinic® Version 03 20.11.2017 – All previous version are no longer valid Seite 5
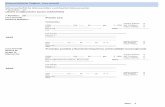
An exemplary SRAclinic® Report is shown in the next figure:
2
3
4
5
1
6
7

Stroke-Risik-Analysis - SRAclinic® Version 03 20.11.2017 – All previous version are no longer valid Seite 6
The SRAclinic® Report is composed of the following areas:
1. Address – can be changed via the personal area of the SRA® platform.
2. Date information – the date of report creation and exam date are displayed.
3. Patient data
The name of the patient can be entered in the Patient name field. *
The entered identification number is shown in the Patient number field.
4. Analysis results – The result of the analysis is displayed here.
5. Hour sections – Number of evaluable hour sections.
6. Lorenz plot – A reference to manifestation of atrial fibrillation on the Lorenz plot is
depicted here.
7. ECG- Start Viewer – All details of the original ECG recording can be accessed
simply and quickly with the SRAviewer®. Especially conspicuous segments from the
Lorenz plot can be attributed to the corresponding ECG data with a mouse click.
* For data protection reasons, no direct personal data are transmitted.

Stroke-Risik-Analysis - SRAclinic® Version 03 20.11.2017 – All previous version are no longer valid Seite 7
Results of SRAclinic®
The following results determined by SRAclinic®:
No risk for paroxysmal atrial fibrillation
Increase risk for paroxysmal atrial fibrillation
Signs of manifest atrial fibrillation
Not analysable
Interpretation of the risk levels
No risk for paroxysmal atrial fibrillation
No episode of manifest atrial fibrillation and no increased risk for paroxysmal atrial fibrillation was detect.
Increase risk for paroxysmal atrial fibrillation
An increased risk for paroxysmal atrial fibrillation was detected, altrough no fibrillation episodes occumed during the entire recording. In the evaluable ECG section no fibrillation episodes were detected. Due to the high sensitivity of the analysis, it is to be assumed that there is very probably no flickering episode. This result, how detects an increased risk for atrial fibrillation in absence from manifest atrial fibrillations, provides the diagnostician before the biggest challenge. The study results and existing literature show that a further search for paroxysmal AF will be much more successful than without preselection in this risk group. How much effort should be operated for advance (more SRA® investigations further long-term ECG, implantable loop recorder...), it also largely depends on many additional diagnostic parameters such as atrial size, mitral regurgitation, etc. from.
Signs of manifest atrial fibrillation
An arrhythmia which has typical characteristics of manifest atrial fibrillation , was detected. A particularly representative ECG section is shown and used for validation. Despite a high specificity , a false positive result can not be excluded. The pictured ECG section has to be checked by a doctor.
Not analysable
It could be performed no analysis due to a bad signal quality , a low voltage or
morphological changes of the QRS complex.

Stroke-Risik-Analysis - SRAclinic® Version 03 20.11.2017 – All previous version are no longer valid Seite 8
Notes:
SRAclinic® is based on the analysis of the rhythm (RR intervals). Further evaluations
such as pathological QRS complex, ST segment elevation, prolonged PR interval,
etc. are not carried out.
SRAclinic® results can be influenced by cardiac pacemakers, strong ventricular
extrasystoles and pharmacological cardioversions. No SRAclinic® analysis should be
conducted in these cases.
5 min. ECG segment:
If manifestation of one or more atrial fibrillation episodes is detected, the sides 2 (channel 1)
and 3 (channel 2) contain the ECG segment, which display it in a particularly illustrative and
representative way. No ECG segment is present during the recording, which displays this in
a more illustrative and representative way.
To ensure that the reliability of detecting atrial fibrillation episodes is at a high level, great
emphasis was placed on a very high sensitivity (even with short episodes) at the request of
many users. As a result, false positive results can also occur, but they are rare and can be
evaluated relatively easily by the supplied 5 min. ECG segment. Many users, cardiologists in
particular, confirmed this procedure to be beneficial.
If the 5 min. ECG segment is incorrectly positive, no atrial fibrillation episodes are in the rest
of the ECG either.
The 5 min. ECG segment is provided with sufficient resolution and can be enlarged up to
400% with a PDF reader without loss.
Example for a 5-minute ECG-Stripe with atrial fibrillation

Stroke-Risik-Analysis - SRAclinic® Version 03 20.11.2017 – All previous version are no longer valid Seite 9

Stroke-Risik-Analysis - SRAclinic® Version 03 20.11.2017 – All previous version are no longer valid Seite 10
Management of SRAclinic® (web platform)
The SRA® platform is available for access to the SRAclinic® Reports, which can be
accessed with user name and password via the homepage www.apoplexmedical.com. All
reports are stored in chronological order here and can be retrieved up to three months after
the evaluation. Starting the SRAviewers® to evaluate the ECG recordings is also possible
from here. The management of personal data (address, email, etc.) is also possible on the
platform as well as the installation of the transmission software if a conventional long-term
ECG recorder is used.
It is possible to access the data with a password from any computer workstation (with
Internet access).
Display of the individual hourly
Lorenz plots
Lorenz plots of the individual
hours in the order from left to right and from top to bottom.
The hour and the signal quality
are given under each plot.
Empty coordinate systems are a sign for non-evaluable ECG data, e.g., due to poor signal quality. Hour sections without contents (no coordinate system) at the end of the overview mean that the ECG recording was stopped.

Stroke-Risik-Analysis - SRAclinic® Version 03 20.11.2017 – All previous version are no longer valid Seite 11
Appendix

Stroke-Risik-Analysis - SRAclinic® Version 03 20.11.2017 – All previous version are no longer valid Seite 12
SRAclinic® for the detection of AF after a stroke

Stroke-Risik-Analysis - SRAclinic® Version 03 20.11.2017 – All previous version are no longer valid Seite 13
The Lorenz Plot
The Lorenz plot provides an excellent method for the visualization of the dynamics of the
heartbeat, often also called the Poincaré Plot. The times between two QRS complexes (RR
interval) are displayed in such a way that an interval is drawn against the next one in a
coordinate system. This can be done in two dimensions (x,y) as shown in the next figure.
Example:
RRn 0
RRn 0
RRn+1
Please note:
The analysis is based on many different
mathematical parameters. Properties of
the Lorenz plots are only a part of these
parameters. Consequently, the result of
the analysis cannot be derived solely from
the Lorenz plot.
The Lorenz plot also provides you with
the possibility of obtaining visual
information about the variability of the
heart rate.

Stroke-Risik-Analysis - SRAclinic® Version 03 20.11.2017 – All previous version are no longer valid Seite 14
The signal quality has decisive influence on the analysis of the data. Please be sure to
follow the instructions for performing good ECG recording.
The display of the signal quality in the SRAclinic® Report allows you to check the recording
quality. The following signal qualities are displayed:
1 - Excellent
2 - Good
3 - Satisfactory
4 - Sufficient – please repeat recording if necessary.
6 - Not evaluable
Note: SRAclinic® is carried out fully automatically and in particular can occasionally lead to
a faulty detection of QRS complexes (R waves) and the detection of ventricular extrasystoles
(VES), which can affect the risk assessment in connection with bad signal quality .
It may happen that SRAclinic® cannot always reliably distinguish between errors and VES or
does not detect all RR intervals. Errors are often manifested in randomly distributed points in
the Lorenz plot (Fig. 1). Missing R waves are indicated by other clubs with double distance in
x and y directions (Fig. 2).
The detection of VES is based on a check of the morphology of the QRS complexes. This
can be influenced by faults in the signal, position of the electrodes, position type of the heart
or by strongly widened QRS complexes with atrial beats (e.g., in the case of thigh
blockades). With strongly widened QRS complexes and signs of manifestation of fibrillation,
no VES detection is carried out. If there is poor signal quality (especially in the case of signal
4) or in case of doubt concerning the QRS detection (conspicuous features in the Lorenz
plot), you should check R wave detection via the ECG Viewer for plausibility and repeat the
recording if needed.
1 2
Note: If signal is not evaluable, you receive a corresponding note in the report. Please repeat
the recording.

Stroke-Risik-Analysis - SRAclinic® Version 03 20.11.2017 – All previous version are no longer valid Seite 15
Repetition of an SRAclinic® examination due to poor signal quality
In order not to create incorrect results, the analysis is canceled in case of insufficient data quality. This
can be happen for different reasons.
Too many artifacts, and consequently not enough R waves for an adequate calculation.
Too small amplitude of the R waves and insufficient detection of the R waves as a result.
The examination, i.e., the ECG recording, must be repeated for all of these ECGs sent in with poor
quality. There are no additional costs but the additional work for reattaching the electrodes, waiting
time for the patients, etc. can be avoided in most cases.
Generally, all recorders on the market fulfill the necessary standards for a good ECG signal. The
problems mostly arise during attachment of the electrodes. There are two basic rules here, which
almost guarantee a good signal when they are followed.
Skin preparation
Only you can ensure good skin preparation on site; a leaflet from apoplexy medical technologies is
provided to help you in this matter.
Electrodes
In tests, we found that different electrodes under the same conditions otherwise produce significantly
different results in ECG quality. Consequently, the quality of the electrode has a measurable impact on
the signal quality.
To give you an idea of the different quality, we employed a cheap disposable electrode on one
channel and a high-quality disposable electrode on the other channel during the same recording.
Example 1:
Fig. 1 Channel 1
Fig. 2 Channel 2 You can see here that it is very difficult on channel 1 to carry out automatic R wave detection, whereas
channel 2 displays a clean QRS complex.

Stroke-Risik-Analysis - SRAclinic® Version 03 20.11.2017 – All previous version are no longer valid Seite 16
Example 2:
Fig. 3 Channel 1
Fig. 4 Channel 2 In this example you can see very clearly that occurring and not always avoidable movement
interference impact the ECG signal differently depending on the electrode quality. You can clearly see
that the signal at the cheap electrode is much more susceptible to interference than at the higher
quality electrode.
While you can tolerate longer phases with poor signal quality in conventional long-term ECG
evaluation, SRAclinic® is dependent on automatically detecting the greatest number possible of R
waves in ECG data.